By General Aviation News Staff · March 14, 2023
They both fly, of course, but a new study finds that honeybees navigate the same way the earliest pilots navigated: By following landmarks on the landscape below — sometimes referred to IFR: I follow roads.
In the earliest days of human flight, before the invention of the first radio beacons and GPS, pilots commonly navigated by following roads and railways — what researchers say are “striking linear landscape elements at ground level that guide towards a destination of interest.”
A century of research has shown that honeybees can navigate by their sense of smell, the sun, the sky’s pattern of polarized light, vertical landmarks that stand out from the panorama, and possibly the Earth’s magnetic field. They are also clever learners that can retain memories to help them find their way home.
Now, scientists have shown that honeybees tend to search for their way home by orienting themselves in relation to dominant landscape elements, just like the first pilots.
In a study published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, scientists have shown that honeybees retain a memory of the dominant linear landscape elements in their home area, such as channels, roads, and boundaries. When transported to an unfamiliar area, they seek out local elements of this kind, compare their layout to the memory, and fly along them to seek their way home.
“Here we show that honeybees use a ‘navigation memory,’ a kind of mental map of the area that they know, to guide their search flights when they look for their hive starting in a new, unexplored area,” said Dr. Randolf Menzel, an emeritus professor at the Department of Neurobiology of the Free University of Berlin, and the study’s lead author. “Linear landscape elements, such as water channels, roads, and field edges, appear to be important components of this navigation memory.”
Tiny transponders
In the late summer of 2010 and 2011 near the village of Klein Lüben in Brandenburg, Germany, Menzel and his colleagues caught 50 experienced forager honeybees and glued a 10.5-mg transponder on their backs. They then released them in a new test area, too distant to be familiar to the bees.
In the test area was a radar that could detect the transponders at a distance of up to 900 meters (2,952 feet). The most notable landmark in the test area was a pair of parallel irrigation channels, running southwest to northeast, according to the researchers.
When honeybees find themselves in unfamiliar territory, they fly in exploratory loops in different directions and over different distances, centered on the release spot. With the radar, the researchers tracked the exact exploratory flight pattern of each bee for between 20 minutes and three hours. The bees flew at up to nine meters (29 feet) above the ground during the experiment.
The researchers collected bees from five hives. The home area around hives A and B resembled the test area in terms of the number, width, length, and angle of linear landscape elements, especially irrigation channels. The home range around hives D and E was highly dissimilar, while the home area around hive C was intermediate in similarity to the test area.
Other landmarks by which honeybees are known to find their way, such as structured horizons or vertical elements that stand out, were absent in the test area.
The researchers first simulated two sets of random flight patterns, centered on the release spot, and generated with different algorithms. Since the observed flight patterns were highly different from these, the researchers concluded that the honeybees didn’t simply conduct random search flights.
The researchers then used advanced statistics to analyze the orientation of flights and their frequency of flying over each 100 x 100 meter block within the test area. They showed that the honeybees spent a disproportionate amount of time flying alongside the irrigation channels. Analyses showed that these continued to guide the exploratory flights even when the bees were more than 30 meters away, the maximum distance from which honeybees are able to see such landscape elements. This implies that the bees kept them in their memory for prolonged periods, the researchers hypothesized.
“Our data show that similarities and differences in the layout of the linear landscape elements between their home area and the new area are used by the bees to explore where their hive might be,” said Menzel.
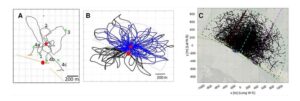
The structure of the search flights. (A) Example of a bee’s search flight (Bee 05 from Home Area E). (B) Example of a simulated bee’s flight. Two models were run, Model S with search loops in all directions (black and blue trajectories) and Model R in which fixes outside the radar range (dashed line) were excluded (only blue parts of the trajectories). (C) All fixes of all search flights plotted together with the radar range (green dashed line) with the release site at the origin. The dashed line (red, cyan, magenta and yellow) highlight the edges of the test site. The red dot is the radar site, the red star is the release site, and the green arrows are the direction of flight. (Image Courtesy Eric Bullinger, Uwe Greggers, and Randolf Menzel)
Navigational memory
Machine learning algorithms showed that the irrigation channels in the test area were most informative for predicting the exploratory flights of bees from hives A and B, less so for bees from hive C, and the least for bees from hives D and E, the researchers reported.
This suggests that the bees retained a navigational memory of their home area, based on linear landscape elements, and tried to generalize what they saw in the test area to their memory to find their way home.
“Flying animals identify such extended ground structures in a map-like aerial view, making them highly attractive as guiding structures. It is thus not surprising that both bats and birds use linear landmarks for navigation. Based on the data reported here we conclude that elongated ground structures are also salient components of the honeybees’ navigation memory,” the researchers concluded.
You can read the full study here.
https://generalaviationnews.com/2023/03/14/what-do-honeybees-have-in-common-with-pilots/